How Is Vitamin E Thought to Play a Role in Reducing the Risk of Heart Disease?
Vitamin E supports your immune system, protects your body tissues, and helps your cells carry out their functions. But how is vitamin E thought to play a role in reducing the risk of heart disease?
In this article, let's explore vitamin E and its role in your heart health.
RELATED: Nail Problems Due To Vitamin Deficiency
How Is Vitamin E Thought to Play a Role in Reducing the Risk of Heart Disease

What Is Vitamin E?
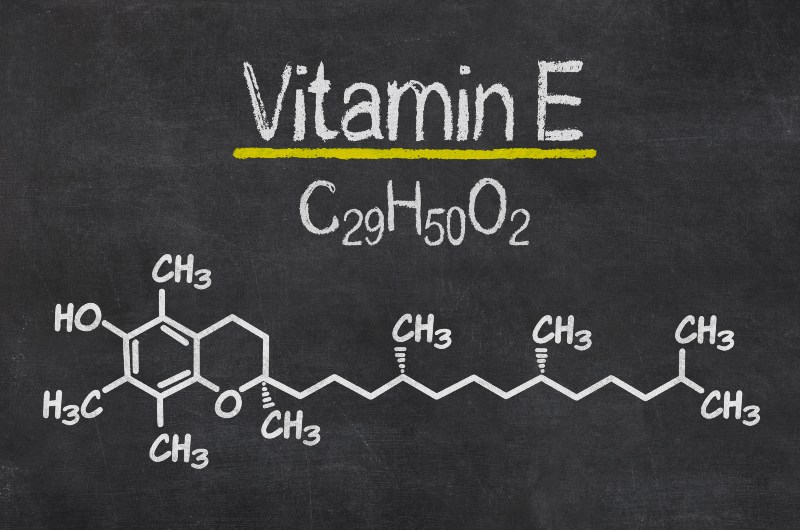
Vitamin E is a nutrient that your body stores in your liver and fatty tissue. It's crucial to the health of your:
- blood and blood vessels
- vision
- brain
- reproduction
- skin
- cell membranes
- immune function
This fat-soluble vitamin comes in eight chemical forms, which include:
- alpha-tocopherol
- alpha-tocotrienol
- beta-tocopherol
- beta-tocotrienol
- delta-tocopherol
- delta-tocotrienol
- gamma-tocopherol
- gamma-tocotrienol
Of all these forms, the human body uses only alpha-tocopherol. It's also the most active and most dominant form of vitamin E.
Alpha-tocopherol possesses antioxidant properties.
An antioxidant is a substance that can protect your cells against the harmful effects of loose electrons or the so-called “free radicals”.
Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage the DNA in your cells. They're produced by your body when:
- breaking down food, or
- exposed to radiation or smoke
The damage caused by these free radicals can lead to health problems, including cardiovascular disease.
How Is Vitamin E Thought to Play a Role in Reducing the Risk of Heart Disease?
Studies show that alpha-tocopherol can serve as a preventive treatment for or delay coronary heart disease, thanks to its antioxidant properties and cardioprotective effects.
It has been viewed to reduce:
- platelet adhesion and aggregation
- the proliferation of smooth muscle cells
- atherosclerotic lesions
- activation of protein kinase C
- oxidation of low-density lipoproteins
- arterial thrombosis
Many parts of your circulatory system have an interior lining referred to as endothelium, which is composed of endothelial cells. Endothelial cells produce substances that control the contraction and relaxation of the muscular wall of your vessels.
Research suggests that following vitamin E supplementation, individuals have shown improvement in their endothelial function.
Other studies also show that individuals who took vitamin E supplements reduced their risk of having a sudden cardiac arrest by 34-39%. Meanwhile, their cardiac mortality reduced by 47%.
However, some clinical trials question the effectiveness of vitamin E supplements when it comes to preventing coronary heart disease.
For instance, a study conducted among almost 10,000 patients, who were at high risk of heart disease or stroke, took 400 IU/day of vitamin E. But they didn't have fewer hospitalizations or cardiovascular events compared with those who took a placebo.
Then, a follow-up study was conducted, and the participants continuously took vitamin E supplements for two and a half years. Results showed that they didn't have any significant protection against unstable angina, stroke, heart attacks, or mortality from cardiovascular disease.
On the other hand, research reveals that vitamin E supplements may have benefits in only specific groups of people.
For example, a trial conducted in Israel found out that individuals with type 2 diabetes, who took high-dose of vitamin E, showed a reduction in heart disease.
Based on these studies, the American Heart Association (AHA) concluded that the use of vitamin E for cardiovascular risk reduction isn't justified.
How Much Vitamin E Should I Take Daily?

Vitamin E, when consumed at the right doses, is safe. However, the values vary by age and condition.
The Food and Nutrition Board developed the following recommended dietary allowances for vitamin E:
- infants (0-6 months): 4 mg/day
- infants (7-12 months): 5 mg/day
- children (1-3 years): 6 mg/day
- children (4-8 years): 7 mg/day
- children (9-13 years): 11 mg
- adolescents and adults (14 years or older): 15 mg/day
- breastfeeding teens and women: 19 mg/day
Remember: Don't overmedicate. Avoid the mindset that “more is better”.
RELATED: Best Vitamins to Keep a Full, Healthy Head of Hair
What Foods Are High in Vitamin E?
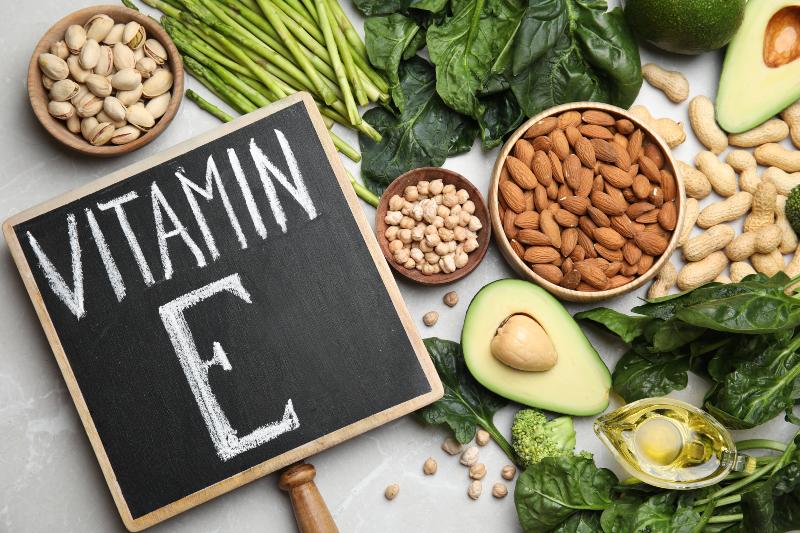

One way to meet the daily requirement of vitamin E is to consume foods that are rich in this nutrient.
Great sources of vitamin E include:
- seeds, like pumpkin and sunflower seeds
- vegetable oils, such as safflower, wheat germ, canola, corn, soybean, and sunflower oils
- nuts, including hazelnuts, peanuts, walnuts, and almonds
- green veggies, like broccoli, spinach, collard greens, beet greens, and asparagus
- fortified foods, such as margarine, fruit juices, and fortified breakfast cereals
- meats
- mangoes
- red bell peppers
- avocados
- pumpkin
You can also take vitamin E in the form of drops or capsules.
However, keep in mind that the highest limit for vitamin E supplements is 1,500 IU/day (natural form) and 1,100 IU/day (synthetic form).
Can Too Much Vitamin E Cause Problems?

Studies show that consuming high doses of vitamin E can harm your health. It can increase the risk of drug reactions or adverse effects. What's worse, it can even increase your risk of dying, especially if you had a previous heart attack.
To be specific, vitamin E overdose may cause hemorrhagic stroke, birth defects, and prostate cancer. On the other hand, low dosage or vitamin E deficiency may result in hemolytic anemia in premature infants.
On some occasions, vitamin E supplements may also cause:
- abdominal pain
- headache
- high creatinine level
- fatigue
- dermatitis
- diarrhea
- gonadal disorder
- blurry vision
- nausea
- weakness
Additionally, vitamin E may interact with other drugs and medical conditions. So consult with your physician before taking vitamin E supplements if you:
- are taking warfarin
- are taking simvastatin
- are taking niacin
- have bleeding disorders
- have head and neck cancer
- have retinitis pigmentosa
- have liver disease
- have vitamin K deficiency
- have diabetes
- are undergoing chemotherapy
- are undergoing radiotherapy
Check out this video by Dr. Eric Berg DC to learn about the best diet if you have heart disease:
Vitamin E has been viewed to decrease your chances of getting cardiovascular disease. However, there's a lack of consistency to back up this claim. Further research is needed to confirm its benefits.g
A more sustainable way to reduce your risk of heart disease and its complications is to take on a healthy lifestyle. Focus on eating healthy and getting active. Quit smoking and manage your blood pressure.
Moreover, consult your physician before you take vitamin E supplements, especially if you have other conditions or are taking other medicines. All of these measures will not only reduce your chances of developing heart disease but prevent other serious risks, too.
Are you currently taking vitamin E supplements? Do you believe that they can reduce your risk of heart disease? Please share your thoughts with us in the comment section below!
Up Next:
- Top 9 Best Vitamins for Men Over 40
- The Health Benefits of Vitamin D
- Intermittent Fasting for Women over 50
Join the healthy living conversation with us on Facebook, Instagram, and Pinterest. We want to hear your story—let’s connect via these channels. Find our community online and join the healthy living revolution today!
Trending
Tongue Color | 7 Scary Tongue Color Meanings
Lecithin Benefits and Side Effects: 10 Surprising Truths
Get Updates
SIGN UP FOR OUR NEWSLETTER TODAY

Tongue Color | 7 Scary Tongue Color Meanings

Lecithin Benefits and Side Effects: 10 Surprising Truths

Related

Tongue Color | 7 Scary Tongue Color Meanings

