Heart attack vs angina. Do you know the difference? Is your chest pain a sign to rush to the emergency room or the doctor's office? Let's find out.
RELATED: How Does a Pulmonary Embolism Kill You
Heart Attack vs Angina
Symptoms, Causes, Treatments

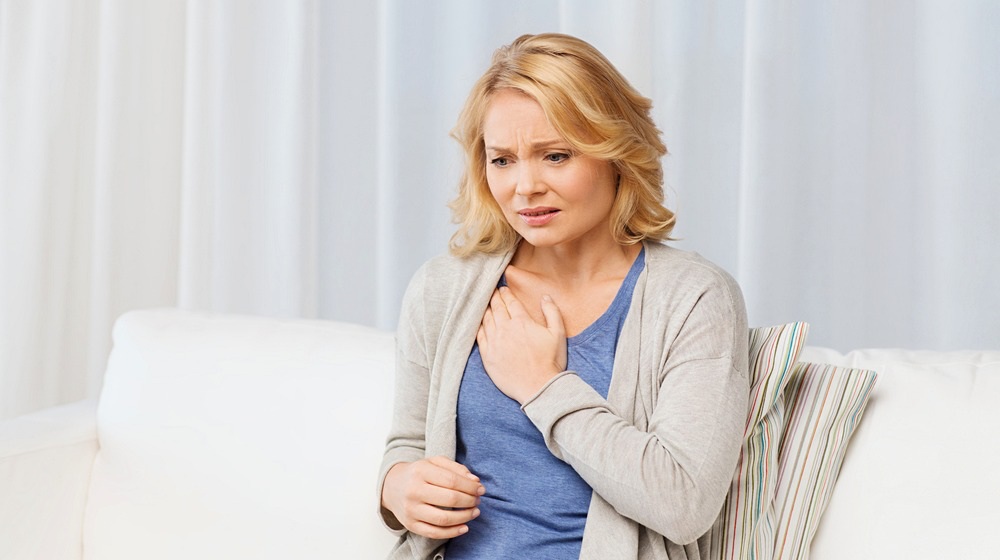
What Is Angina?

Angina is chest pain, which occurs when plaque build-up in your arteries and not enough blood gets to your heart. It is a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Your coronary arteries are the vessels that deliver blood-rich oxygen to your heart.
There are two main types of angina:
- Stable angina follows a pattern. It typically happens after you exert yourself like going on a hike or a long walk. You can manage stable angina with medication and rest.
- Unstable angina is more difficult to predict and happens with no obvious trigger.
Stable angina could progress to unstable angina. In some cases, unstable angina occurs without experiencing stable angina episodes first.
Symptoms

Symptoms of stable angina include:
- pressure or pain in your chest (lasting 5 minutes or less)
- discomfort in your jaw, neck, shoulder, arm, and back
It could be triggered by:
- physical exertion
- heavy meals
- exposure to hot or cold temperatures
- smoking
Symptoms of unstable angina include:
- more severe pain than stable angina
- could last over 30 minutes
Unstable angina episodes come unexpectedly even while resting. Your angina medication may not relieve your chest pain.
If you notice that your chest pain happens more and more frequently, rush to your doctor and head to the emergency room. Unstable angina could progress and may be a signal of a heart attack.
Causes
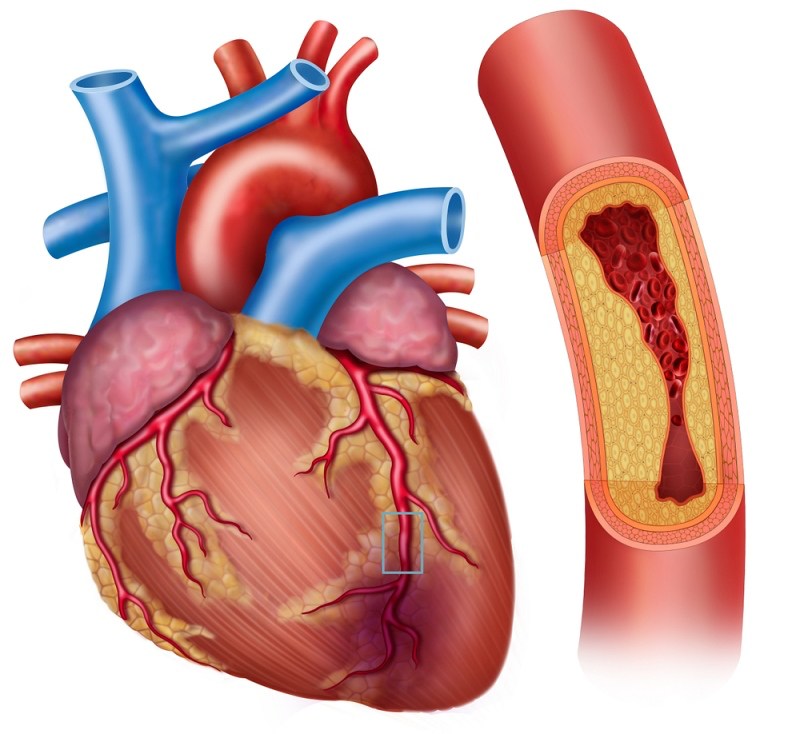
It's usually caused by the build-up of plaque in your blood vessels (coronary artery disease or atherosclerosis).
It's important to understand what activities trigger your episodes to manage to help manage your symptoms. Your doctor may also recommend heart-healthy dietary and lifestyle changes.
Treatments
If you have never experienced chest pain or an angina episode, do not hesitate to call for medical emergency services.
If you have been diagnosed with angina, your doctor would have prescribed you medication like GTN (glyceryl trinitrate).
- Stop what you're doing.
- Rest.
- Take your medication.
- Wait for five minutes.
- Take another dose if the chest pain recurs.
- Wait another five minutes.
- If the pain returns, treat it as a heart attack and call for help.
Long-term treatments for angina may include angioplasty and heart bypass surgery.
RELATED: Protect Your Heart with These 13 Natural Blood Thinners
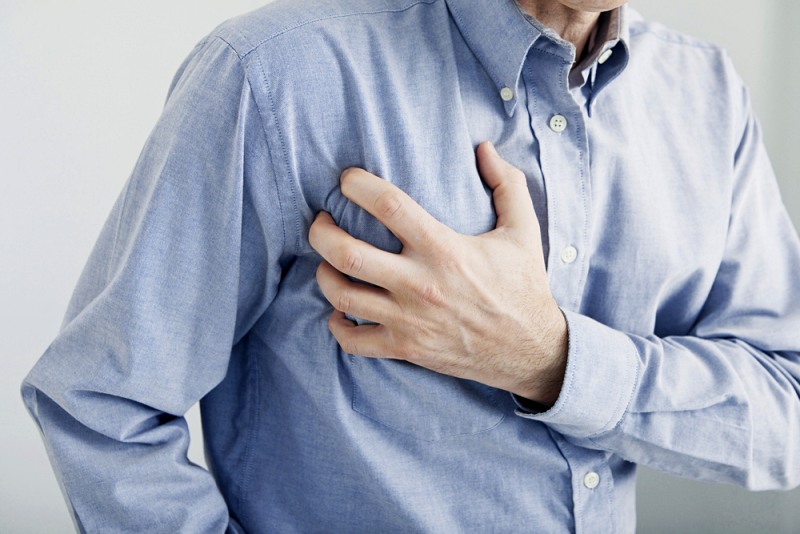
What Is a Heart Attack?

A heart attack is a medical emergency where your vessels are severely or completely blocked and blood-rich oxygen can't make its way to your heart.
The lack of oxygen injures your heart. The severity of the damage depends on the size of the affected arteries. You may recover from a heart attack with proper management and lifestyle changes.
Unlike a heart attack, angina is not damaging to your heart.
Symptoms

Some warning signs and characteristics of a heart attack may include:
- tightness, pressure, squeezing pain in your chest
- lasts for minutes
- may come and go
- shortness of breath
- pain in your neck, jaw, shoulders, back, arm (one or both), stomach
- cold sweat
- nausea
- vomiting
- lightheadedness
Everyone experiences different symptoms. Err on the side of caution and get help when you feel any chest pain.
Causes
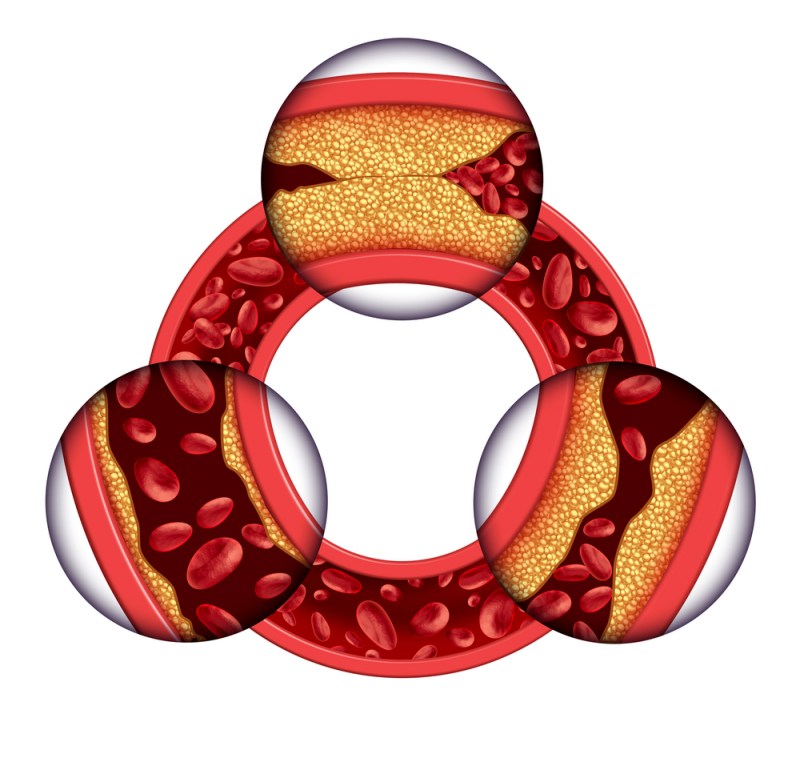
A heart attack is usually caused by plaque buildup restricting oxygen-rich blood from reaching your heart, but other possible causes may include:
- spasming of a coronary artery
- tear in a coronary artery wall
You can lower your risk of suffering from this medical emergency by:
- avoiding alcohol, smoking
- controlling your cholesterol levels
- managing your blood pressure
- exercising
- losing excess weight
- lowering your risk of diabetes
- managing your stress levels
- eating a heart-healthy diet
Treatments

Fortunately, heart attacks are not always fatal. Many people recover and lead normal and productive lives after suffering from a heart attack.
Recovery could take weeks and your treatment would depend on the type of heart attack you experienced.
Your doctor may prescribe your medication like:
- anticoagulant
- antiplatelet agent
- ACE inhibitor
- angiotensin II receptor blocker
- angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor
- beta-blocker
- a combination of alpha- and beta-blocker
- calcium channel blocker
- cholesterol-lowering medication
- digitalis preparation
- diuretics
- vasodilator
Common procedures may include:
- angioplasty
- artificial heart valve surgery
- atherectomy
- bypass surgery
- cardiomyoplasty
- heart transplant
- minimally invasive heart surgery
- radiofrequency ablation
- stent procedure
- transmyocardial revascularization (TMR)
Work closely with your doctor to find the best treatment plan for you. In addition to medication and procedures, you will likely need to exchange your diet and lifestyle for a heart-healthier one.
Many people can live long and productive lives even after a heart attack. The next step is to prevent a second one.
Monitor your risk factors and ask your doctor exactly what you need to change to improve your chances. See your cardiologist regularly to see how your heart is doing, and to check if you need to change your medication.
Angina vs Heart Attack

Angina is a symptom of heart disease, while a heart attack is an emergency situation caused by heart disease. Angina is a term for chest pain, while a heart attack is a condition whose symptoms include chest pain.
A heart attack also comes with other symptoms such as pain that radiates to other parts of your body. And you might find yourself nauseated and sweating. It also leads to heart muscle injuries, whereas angina does not.
If you do experience any chest pain, don't hesitate to call for help. The safest course of action is to get the help of medical professionals.
Check out this video to learn the differences between angina vs heart attack:
Taking better care of your heart by exercising, eating healthily, and avoiding smoking and alcohol could improve your heart health. By doing these, you can lower your risks of both angina and heart attack.
Are you more confident than you can tell the difference between angina and a heart attack? Are there other unexplained pains you need help uncovering? Let us know in the comments section below!
You Might Also Like:
- Discover What Causes Left Side Pain under Ribs: 8 Possible Causes
- Angina Attack What to Do | Treatment for Angina
- How to Burn Fat While Sleeping | 9 Stress-Free Ways to Burn Fat While Sleeping
Join the healthy living conversation with us on Facebook, Instagram, and Pinterest. We want to hear your story—let’s connect via these channels. Find our community online and join the healthy living revolution today!
Trending
Get Updates
SIGN UP FOR OUR NEWSLETTER TODAY



